Why KRIs are important for an organization? KRIs are indicators of the ongoing changes happening in the risk profile of an organization. KRIs enable an organization to be proactive in taking risk prevention/protection actions in a timely manner.
KRIs
- Highlight the current risk profile of an organization by providing a measure of the status of identified risks and the effectiveness of risk mitigation controls in place;
- Highlight the trends and changes happening in the risk profile of an organization by monitoring changes in risk levels between consecutive Risk & Control Assessments (RCSA);
- Provide early warning signals through predictive risk indicators which will highlight changes in the risk, control environment, control effectiveness and potential risk issues, before they occur which will result in loss and other exposure; and
- Enable actions that will prevent or minimize material loss caused by risk
How to select the right KRIs
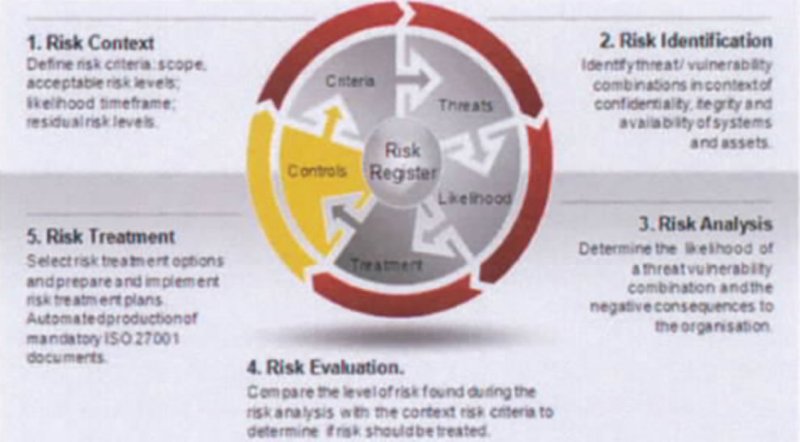
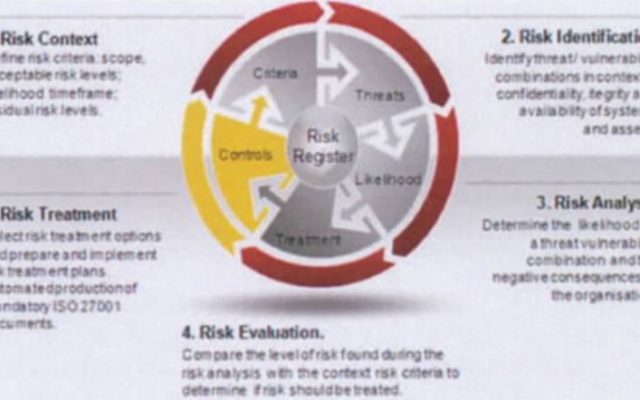
The following are the key considerations while selecting the KRIs in an organization
- It should provide “early warning” signals to proactively take actions that will help in reducing potential risk exposures;
- It should indicate past, current and projected level of risks and can be used as a criteria to monitor, escalate and manage risk and risk mitigation controls,strategy and plans.
The following are the sources of information which will help organizations in identifying significant risks and subsequent KRIs identification
- historical internal loss events;
- results of risk and control self assessments;
- internal / external audit findings;
- regulatory audit findings; and
- workshops / discussions with business functions e.g. Finance, Human resources.
How to implement KRIs in an organization
From a practical standpoint, KRIs need to be built into the operational and business processes of an organization in an integrated manner.The following are some of the facts to be considered in the implementation of KRIs in an organization:
- Building KRIs based on legacy operational and business processes is likely to be an expensive and potentially impractical proposition for many organisations;
- Introducing KRIs for most organisations is most practically undertaken as an integral part of new system development and process transformation initiatives where the cost is likely to be much lower and work will be less complex;
- Internal auditors should provide support and assurance that KRIs selected are focused on key risk areas and are robustly implemented, such that they support risk monitoring and decision making process of an organization very effectively;
- Suitable Software need to be considered for KRI Tracking Automation
- Owners should be assigned for individual KRIs who will be responsible for collection and collation of data related to the KRIs assigned to them; and
- Data on KRIs should be collated on a systematic and consistent basis in order to be meaningful, e.g. on a monthly/quarterly basis.
- Key risk indicators will evolve over time. Analysis of actual losses and near misses will assist in identifying which KRIs are the best at giving early warning and allowing timely action. Periodic review needs to take place of the indicators themselves and their associated thresholds to ensure they remain aligned with the dynamic of the business environment and the significant risks faced by the franchisee at any point in time.
The below seen is a list of sample KPIs from Operations Risk perspective
- Average length of tenure of services of staffs
- Average time to fill open positions
- Staff turnover rates
- Number of customer complaints
- Number of compliance / regulatory breaches
- Number and security incidents
- Unplanned systems downtime
- Number of open system change requests
- Number of pending help desk calls
- Number of physical security incidents
Article by channel:
Everything you need to know about Digital Transformation
The best articles, news and events direct to your inbox
Read more articles tagged: Featured