Data Asset Management (DAM) conserves, curates and exploits valuable enterprise Data Assets – Enterprise Data along with their associated Services. Data Assets are now widely regarded as important in driving business value.
Just as other tangible assets are monetised, Enterprise Data and Services have a fiscal value on the balance sheet. Business Value is extracted from Enterprise Data and Services through Data Asset Management – driving Data Innovation facilitating the launch of new data products and services in the Data Economy – and Competitiveness Achievement Planning (CAP) which delivers enhanced operational performance and accelerated business results.
Every day, in every organisation, the massive volume and diversity of decisions and actions which are informed by analytics and insights derived from Enterprise Data – are increasingly driven by new and evolving Data Asset Management frameworks, data architectures and technology platforms.
In every industry sector, companies are in a race to accumulate unique data assets and develop data exploitation methods – before their competitive rivals outmanoeuvre, outpace and outperform them. Those companies which do not see data as a core enterprise asset, or are unable to develop a Data Asset Management Strategy are in danger of decline – and ultimately risk business failure.
Data Asset Management (DAM) – Information Maturity Model (IMM)
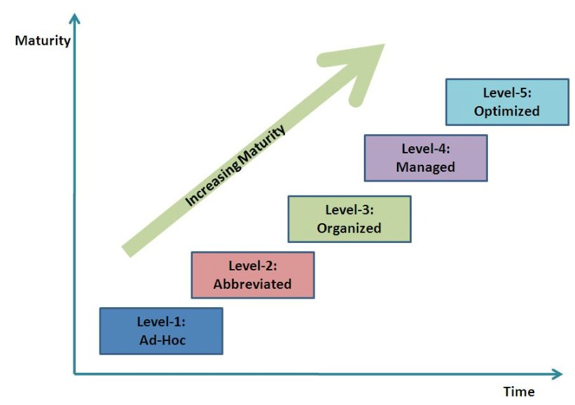
Many organisations are now changing the way in which they design and manage their business and technology portfolios, plan, design and execute their Data Business Transformation programmes and projects – through Data Asset Management (DAM) – bringing a more successful and efficient way to continuously improve the daily execution and outcomes of core operations and processes.
Data Asset Management – when adequately funded, planned and organised – has the potential to generate significant business impact in every public and social enterprise through business strategy enablement.
Data Asset Management architectures, methods and techniques, Data Services and platforms support Data Innovation in the creation of novel data products and services, and can drive Competitiveness Achievement Planning (CAP) in delivering accelerated business performance.
Data Asset Management (DAM): –
- Data Asset Models – Enterprise and Domain-level Data, Service and Information Models
- Data Architectures – Business and Technology Data Architectures and Roadmaps
- Data Technology Platforms – Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud Platforms
- Data Asset Management Frameworks – Enterprise Data and Service Frameworks
- Fast Data Appliances – In-memory Computing – GPGPUs / SSDs (SAP HANA)
- Big Data Platforms – Hadoop Clusters, Spark (Cloudera, Hortonworks, MAPR)
- Data Science Platforms – Propensity and Predictive Models, Analytics and Insights
- Artificial Intelligence Platforms – Artificial Intelligence (AI) / Machine Learning
Novel business models and data architectures can be created by assembling and integrating these new data Assets together in surprising and inventive ways – such as Social Intelligence, Lifestyle Analytics and Consumer DNA.
Data-driven features and functions are now possible such as micro-marketing and mass customisation – the specific tailoring of products and services that meet the unique needs of every individual consumer – are now easily achievable through Data Innovation, providing not only new means of generating competitive advantage and opening new markets, but also yielding radical improvements in operational effectiveness and accelerated business results.
Data Asset Management (DAM) – Information Maturity Model (IMM)
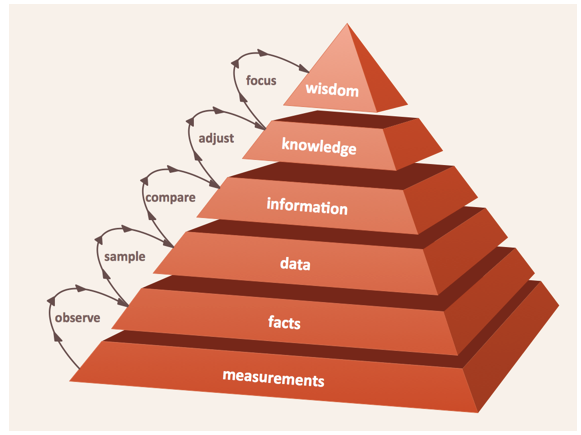
Data Assets – Enterprise Data and Services – are neither an abundant nor a readily available resource. Data Assets may be decomposed into a vast array of scarce, unique, valuable and often hard-won Data Points and Apps. Each Data Point is defined by its shared Metadata (format) and by its specific Content (values).
Data Point occurrences may be characterised as being either structured Transactional, Event-based data consisting of temporal (historic) and spatial (geographic), personal (demographic), locational (place), fiscal (monetary), conditional (status) and transactional (event) data item values – or described as unstructured text, image, audio and video stream data content.
Each Data Point is associated with its own specific set of applications (Data Services), sources, costs and benefits. Just as businesses cannot participate in new data markets and economies without the necessary seed funding or capitalisation – similarly, those same businesses cannot generate new propensity models or pricing plans without investment in the data and algorithms to support them.
Data Asset Management (DAM) – Frameworks: –
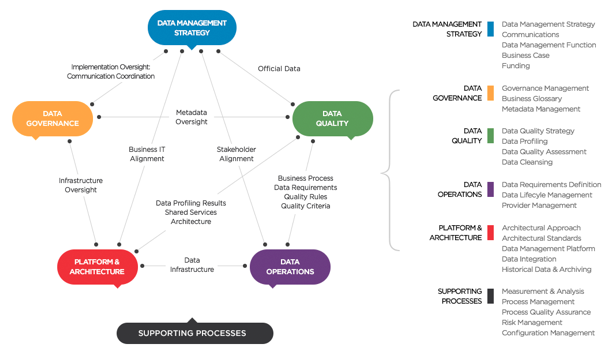
Data Asset Management – along with the data architectures and technology platforms which enable and support DAM – contains of a set of Enterprise Data Frameworks which in turn consists of methods, techniques and processes to execute Enterprise Data Management tasks and decisions.
Enterprise Data Frameworks: –
- Governance – audit, reporting and controls
- Availability – robustness, reliability, resilience
- Performance – velocity, voracity and volume
- Quality – standards, compliance, traceability
- Procurement – identification and capture
- Curation – indexing, cataloguing and annotation
- Management – storage, access and security
- Communication – retrieval, publishing and distribution
Data Asset Management supports the key Enterprise Data requirements of velocity, voracity, and volume – enabling the transformation of traditional hosted local Enterprise Applications (ERP, CRM, DWH and BI) into a set of robust, resilient and reliable SMAC (Social, Mobile, Analytics, Cloud) Data Services available commercially from vendors – easy to procure, install, implement, use and exploit.
These new SMAC Data Assets are delivered over the Internet and hosted as public, private or mixed cloud services. SMAC Data Assets must also integrate with Legacy Enterprise Solutions to be effective. Some heritage corporate data centres may be reinvented – as private clouds providing existing legacy functionality through new and reconfigured SMAC Data Assets.
The enhanced capabilities and capacity released by SMAC Data Assets will not only yield radical improvements in operational efficiency, but also release further opportunities for strategic competitive advantage.
Competitor Advantage is driven by deploying Data Science / Big Data / Fast Data, powering Analytics and Insights, with API Services accessing Cloud Computing and other 3rd Party consumer platforms: –
SMACT/4D Data Technology Stack: –
- Social Media | User Content
- Mobile Platforms | Smart Devices | Smart Apps
- Analytics | Data Science | Big Data – Hadoop, Spark | Fast Data – GPGPUs, SSDs
- Cloud Services Platforms – AWS, Azure, NetSuite, Salesforce, Workday
- Telematics – Machine-generated | Automatic Data Streams | IoT
- 4D Geospatial Data Science | Geo-demographics | GIS Mapping and Spatial Analysis
New Capabilities from DataAsset Management
Data Asset Management, with its hybrid-cloud architecture and collaboration between open-source and commercial software, provides the mechanism for the proliferation of Data Services – presentation and process execution, data management and integration, analytics and insights. All of this, however, requires significant investment. Many enterprises are committing to this investment because of the new capacity and capabilities that the Data Asset Management approach releases.
- Data-driven Customisation.
Data Assets support data-driven Customisation features and functions in areas such as micro-marketing and mass customisation – the specific tailoring of products and services to meet the unique needs of every individual consumer. Machine Learning algorithms increase accuracy over time, by processing more input data over many cycles to enhance propensity and predictive models. Discovering what works under which conditions and for how long requires iterative experimentation, repeated over many system cycles. Data Assets makes these trials more cost-effective to run both as scheduled and ad-hoc jobs – with the capability to modify experimental parameters ‘on the fly’.
- Internal and External Data Markets.
In addition to end-user analytics for standard, recurring questions and ad-hoc analytics for ‘power users’, Data Services offer the possibility of accessing internal and external data markets that satisfy spot demand for new intelligence products and extended data consumption. Visual and Graphical interfaces to internal and external data lakes empower data scientists and other key stakeholders to browse for and access new datasets in the same way as they might shop for commodities on any e-commerce site. Data Applications that visually discover, profile, transform, combine and display both internal and external data, now bring the actual cost of exploring a new risk factor or commercial opportunity below the opportunity cost of failing to investigate the issue.
Many companies collect data that they then share with other organisations, perhaps after further processing – enrichment and enhancement (combining or ‘mashing’ with other data sources) or anonymization (scrubbing proprietary and personal identification information). Some of that data may be of significant interest to their trading partners or to other interested parties in their supply chain. Other data may prove commercially valuable to unrelated external organisations – including demographic data aggregators (Sky IQ, Experian, Dunnhumbey or CACI) – or government agencies.
- Embedded Analytics
Embedded analytics in applications encourage users towards planed and desired outcomes – for example, converting ‘propensity to buy’ into ‘purchase intent’. These include next-best actions for call-centre agents, product placement recommendations, and progress metrics in mobile apps that drive goal-seeking – encouraging consumers to achieve specific outcomes, goals and objectives.
- Data-on-demand Services.
Data can now be procured as an on-demand service – provisioned and managed just like any other on-demand service. Many companies – Social Media Platforms, Audio and Video Streaming Services, Geodemographic Information providers, Airports, Railway and Bus Stations, Hotels and other Media, Travel and Leisure companies – create methods for internal and external applications to obtain data on demand via automated Application Programming Interface Services (APIs) – cutting the cost of new and existing data stores and increasing the Business Value of Data Assets in numerous ways.
Data Asset Management (DAM) – Architecture Roadmap: –
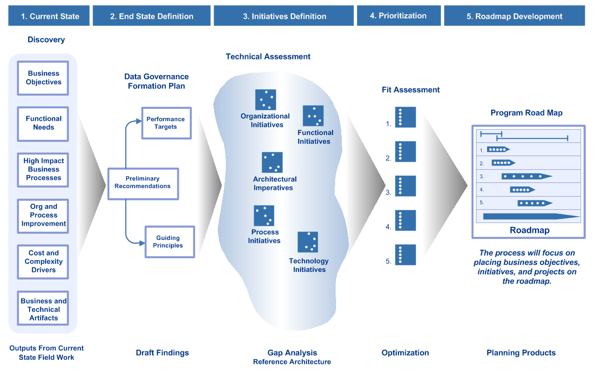
CONCLUSION
Data Assets will extend the influence of algorithmic analytics and insights and so radically improve the outcomes of human decision making. As managers incorporate more data into their decision-making processes, more problem / opportunity domains will have their embedded logic exposed. Those choices once thought to be strictly the domain of human beings will become the province of machines.
This has already happened with consumer product placement recommendations, delivery routing, and credit approvals. Complex applications such as algorithmic analysis of cancer-screening images in Data Healthcare which are largely experimental today – will become routine tomorrow.
Article by channel:
Everything you need to know about Digital Transformation
The best articles, news and events direct to your inbox
Read more articles tagged: Data Management, Featured









