Technology Disruption through Digital Transformation is a high-impact catalyst for Economic Restructuring across global markets – generating enhanced business performance and accelerated sales revenue through novel and innovative Digital Business Operating Models.
Digital Strategy – Problem / Opportunity Domain
The key challenges for enterprises thinking about Digital Business Transformation are: –
- Digital Strategy – what needs to be done?
- Digital Transformation – how can we do it?
Digital Frameworks help businesses across all industry sectors to successfully embrace Digital Transformation so that they can achieve better business outcomes.
This is how a Digital Framework solves your Digital Business Transformation problems: –
- Digital Strategy Framework – a strategy development framework that defines the digital evolution of an organisation and plans successful Digital Transformation.
- Digital Transformation Framework – a change framework that clearly states the Activities and Tasks required by an organisation to manage Digital Transformation.
This is what you can successfully deliver when you use Digital Frameworks to help you exploit your Digital Business Transformation opportunities: –
- Digital Architecture Roadmap – a concise map describing the ‘direction of travel’ for the enterprise digital journey, signposted as a series of achievable milestones;
- Digital Business Model – a vivid articulation of the Digital Enterprise Landscape developed through digital transformation, defined as an Enterprise Target Operating Mode (ETOM);
Digital Business Transformation is the profound and accelerating transformation of enterprise business models, processes, services, activities and competencies to fully leverage the changes and opportunities presented by the twin disruptive forces of global change; Globalisation – the free movement of People, Ideas, Goods, Machinery and Money (Capital Disruption) in a dynamic global economy; coupled with Digital Technology Innovation (Technology Disruption) – together driving the creation of new business models which generate growing data and revenue streams from novel and desirable products and services.
Globalisation and Technology Innovation are simultaneously giving birth to emerging digital industries, markets and economies – evidence of the geopolitical and economic paradigm shifts which are now taking place, shaping change across every aspect of society.
Figure 1: – Digital Business Strategy – Implementation Pathways
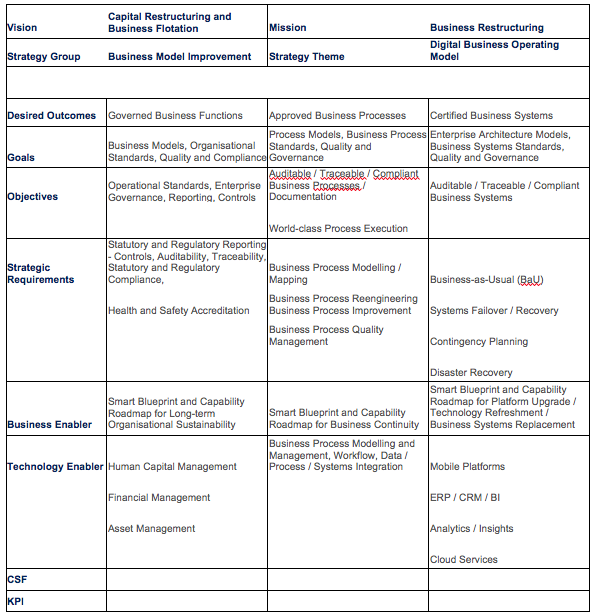
The Vision for Digital Business Transformation is that Digital Innovation is driven by Technology Disruption, and Mission, Strategy Themes / sub-themes that could usefully be explored include: –
Vision: – Digital Innovation through Technology Disruption
Mission: – Create Digital Business Operating Models to enable and support Digital Innovation
Strategy Theme: – Digital Marketing and Social Intelligence
- Outcome – Digital Transformation – Increase On-line Sales by 40% over 3 years
- Goals – the Mapping and Alignment of Business v. Technology Digital Architectures
- Objectives – Aggressive Investment Policy for adoption of disruptive Digital Technologies
- SMAC Digital Technology Stack – supports Innovation and Growth
- Process Automation – enables On-demand / Utility Computing
- Artificial Intelligence – improves Event Outcomes, Goals and Objectives
- Cloud Infrastructure – provides Platform Serviceability, Stability and Security
Technology Disruption drives Digital Innovation – generating new opportunities from novel and innovative methods of production, distribution and communication which enable and support the enhanced digital capability and capacity of business models, people, processes and technologies.
Figure 2: – Digital Omni-channel Retail Strategy – Implementation Pathways
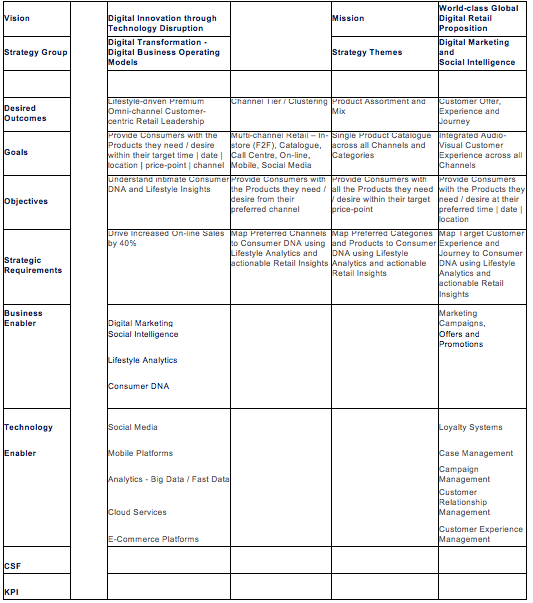
Digital Business Transformation is defined by the adoption of Next Generation Enterprise (NGE) Digital Business Operating Models and other resources – including SMACT/4D Digital Technology Stacks – to create and exploit new business opportunities in digital (virtual) and “bricks and mortar” (physical) economies – radically disrupting existing business models.
Technology Disruption is the mechanism which drives Digital Innovation through the adoption of new production, distribution and communication methods so that new industries, products and services replace outdated ones.
SMAACT/4D Digital Technology Stack: –
- Social Media | User Content – Lifestyle Analytics and Consumer DNA
- Mobile Platforms | Smart Devices | Smart Apps | MEAPs | MADP
- Analytics | Data Science | Big Data – Hadoop, Spark | Fast Data – GPGPUs, SSDs
- Algorithmic Computing | Machine Learning | Artificial Intelligence
- Cloud Services Platforms – AWS, Azure, NetSuite, Salesforce, Workday
- Telematics – Remote Devices | Automatic Data Streams | Smart Grid | IoT
- 4D Geospatial Data Science | Geo-demographics | GIS Mapping | Spatial Analysis
Digital Innovation is driven by Technology Disruption through developing and exploiting new and improved digital competencies and qualities in people, processes and technologies – creating digital business models generating novel and attractive digital products and services – thus unleashing the opportunity to participate in innovative digital markets, emerging industries and virtual economies.
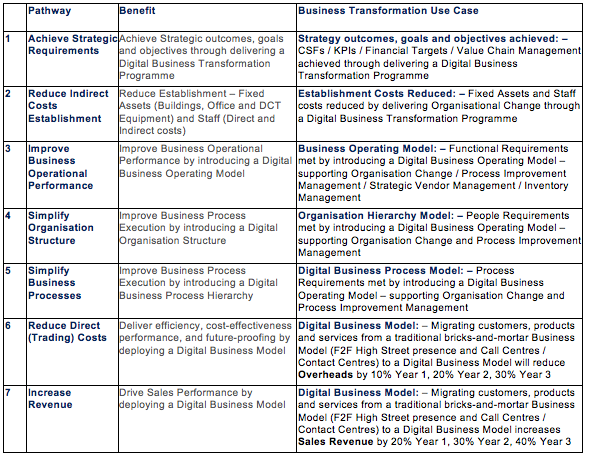
Figure 3: – Digital Business Transformation – Value Pathways
- Thinking about the Future – Strategic Management Framework •
The role of Digital Strategy is to provide strategic analysis and future direction to those key client leadership team members charged with delivering critical Digital Business Transformation and Digital Asset Management (DAM) initiatives.
The challenge is to align and integrate Future State Digital Narratives from different stakeholders – Data and Process Owners, Stewards, Administrators and Operatives, Information Providers and Consumers, Profit Centre and Cost Centre Budget Holders and Responsible Managers in core and shared service functions across the Enterprise – Strategy and Planning, Finance and Accounting, Budgeting and Forecasting, Sales and Marketing, Human Capital – all with multiple, divergent views, drivers, interests, resources, requirements, issues and concerns.
Peter Bishop and Andy Hines, formerly Professors at the University of Texas Futures Studies School at the Houston Clear Lake site – have developed a definitive Strategic Management Framework – Thinking About the Future.
- FRAMING AND SCOPING •
This important first step enables organizations to define the purpose. focus, scope and boundaries of the Political, Legal, Economic, Cultural, Business and Technology problem / opportunity domains requiring resolution. Taking time at the outset of a project, the Strategic Foresight Team defines the Digital Business Transformation domain, describes the required outcomes, goals and objectives and outlines future Sources and Applications of Funds (Cash Flow) and Value Chains (how new Business Processes create and consume Business Value – Assets) – and determines how best to achieve them.
Strategy Study Definition – Problem / Opportunity Domains: –
- Definition – Focus, Scope, Purpose and Boundaries
- Approach – What – How – Why – Who – When – Where?
- Digital Opportunities and Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Sources and Applications of Funds (Cash Flow) and Value Chains (Assets)
- Justification – Cost, Duration and Resources v. Future Benefits and Cash Flows
- ENGAGING •
This second phase is about stakeholder management – developing action agendas for mobilising stakeholders and opening communications channels, soliciting collaborative participation and input. This could involve staging a wide range of Stakeholder Events, organising Strategy Communications, Target-setting and Action Planning, establishing mechanisms for reporting actual achievement against targets – in order that the Strategic Foresight Team engage a wide range of stakeholders, presents a future-oriented, customer-focussed approach and enables the efficient delivery of Digital Business Transformation Strategy Study artefacts & benefits in planned / managed work streams.
Strategy Study Mobilisation – Stakeholder Engagement: –
- Communication Strategy
- Benefits Realisation Strategy
- Digital Strategy Study Programme Plan
- Stakeholder, SME and TDA Strategy Study Launch Events
- RESEARCH – HORIZON SCANNING, MONITORING AND TRACKING •
Once the Strategic Foresight Team is clear about the Digital Business Transformation Strategy Study engagement boundaries, purpose, problem / opportunity domains and scope of a Strategy Study – they can begin to scan both internal and external environments for all relevant input content – information and data which describes global extrapolations, patterns and trends which may indicate emerging transformation drivers and catalysts of change – and to search for, discover and identify any Weak Signals indicating the potential for future disruptive Wild Card or Black Swan events
Strategy Investigation – Content Capture: –
- Emerging Factors and Catalysts of Change
- Internal and External Content, Information and Data
- Digital Transformation Extrapolations, Patterns and Trends
- Horizon Scanning, Monitoring and Tracking Analytics Systems and Cloud Infrastructure
- STRATEGY DISCOVERY – STAKEHOLDER EVENTS & STRATEGY THEMES •
Here we begin to identify and extract useful information from the mass of Research Content that we have discovered and collected. Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions begin to emerge from Data Set “mashing”, Data Mining and Analytics against the massed Research Data – all curated through the human processes of Cognitive Filtering and Intuitive Assimilation of the aggregated information – executed through Digital Business Transformation Strategy Discovery Workshops, Strategy Theme Forums, Value Chain Seminars, Special Interest Group Events and one-to-one Key Stakeholder Interviews •
Strategy Discovery – Content Analysis: –
- SWOT / PEST Analysis
- Data Set “mashing”, Data Mining and Analytics
- Stakeholder, SME and TDA Strategy Discovery Events
- Digital Opportunities and Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Competitor Identification and Rival Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Discovered Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions
- THREAT ANALYSIS – MANAGING UNCERTAINTY •
It has long been recognized that one of the most important competitive factors for any organization to master is the Management of Uncertainty. Uncertainty is the major intangible factor contributing towards the risk of failure in every process, at every level, in every type of business – Social, Public and Private Enterprise.
The way that we think about the future must mirror exactly how the future unfolds. As we have learned from recent experience, the future is not a simple Utopian extrapolation of the past – a continuation of linear, single-domain trends leading inexorably to our preferred vision of the Future.
If all future timelines were linear in nature – then every event would unfold in an unerringly predictable manner towards a known and certain conclusion. This is clearly not the case…
In most organizations, many stakeholders, when left unchallenged, tend to believe that various threat scenarios – as discovered through SWOT / PEST Analyses – are going to play out pretty much in the same way as they have always done.
When the Strategic Foresight Team probes an enterprise’s view of the future, they usually discover the stakeholders vision of their Preferred Future in an array of unexamined, unchallenged, unexplained future assumptions which either maintain the current status quo – or converge around a few clusters of small, linear, incremental future extrapolations.
The future is, however, both unknown and unknowable (Hawking Paradox). Events exist as a thread through a stack of Temporal Planes. The Future is Dystopian – complex and chaotic – with many possible, probable and alternative future outcomes.
Future timelines are non-linear (branched) with an infinite multitude of possible, probable and alternative futures – rendering future outcomes uncertain and unpredictable. We must now consider ways in which the interaction of random, chaotic and radically disruptive events may be factored into enterprise strategy, threat assessment and risk management frameworks and incorporated into decision-making structures and processes •
Threat Analysis: –
- Threat Research and Identification
- Managing Uncertainty, Chaos and Disruption
- Threat Analysis, Assessment and Prioritisation
- Digital Transformation, Factors and Catalysts of Change
- Identified Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions
- STRATEGIC FORESIGHT •
The prime activity in the Strategic Foresight Process is, therefore, to challenge the status quo future state viewpoint and provoke the organisation into thinking seriously about the possibility that things may not continue the same as they have always done – and in fact, rarely do so.
Strategic Foresight processes should therefore include searching for and identifying any potential Weak Signals in the environment predicating future Wild Card and Black Swan events.
In doing so, we could reveal previously hidden factors and catalysts of change – thus exposing a much wider range of challenges, issues, problems, threats, opportunities and risks than may have been considered previously •
Strategic Foresight – Value Chain Analysis: –
- Horizon Scanning, Tracking and Monitoring
- Weak Signals, Wild Cards and Black Swan Events
- Digital Opportunities and Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Competitor Analysis and Rival Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Value Chain Analysis – factors that may enhance or erode Cash Flow and Value
- Analysed Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions
- Horizon Scanning, Monitoring and Tracking – Cloud Analytics Systems and Infrastructure
- SCENARIO FORECASTING AND IMPACT ANALYSIS •
Scenarios are stories about how the future may unfold – and how that future will impact on the way that we work and do business with our business partners, customers and suppliers.
The Strategy Study considers a broad spectrum of possible scenarios as the only sure-fire way to develop robust strategic responses that will securely position the Strategic Foresight Programme to deal with every opportunity and threat domain that may transpire.
The discovery of multiple scenarios and their associated opportunity / threat impact assessments, along with their probability of materialising, Cash Flow and Business Value – covers a wide range of possible and probable Opportunity / Threat situations – with a rich diversity of POSSIBLE, PROBABLE, PREFERRED and ALTERNATIVE FUTURES •
Scenario Forecasting and Impact Analysis: –
- Possible, Probable, Preferred and Alternative Future Scenarios
- Clustered Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes
- Future Business Models and Value Propositions, Products and Services
- Digital Opportunities and Market Value Propositions (MVPs) Scenarios
- Competitor Evaluation and Rival Market Value Propositions (MVPs) Scenarios
- Value Chain Forecasting – Scenario contribution to Cash Flow and Value Chain Models
- Scenario Forecasting and Impact Analysis – Cloud Analytics Systems and Infrastructure
- Forecast Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions
- STRATEGY VISIONING, FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT •
After forecasting has laid out a range of potential Future Scenarios, visioning comes into play — generating a pragmatic view of our “preferred” Future Environment – thus starting to suggest stretch goals for moving towards our “ideal” Strategy Models – using the Strategic Principles and Policies to drive out the “desired” Vision, Missions, Outcomes, Goals and Objectives •
Strategy Visioning, Formulation and Development: –
- Strategic Principles and Policies, Guidelines and Best Practices
- Digital Strategy Themes and Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Competitor Ranking and Rival Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Strategy Models and desired Vision, Missions, Outcomes, Goals and Objectives
- Proposed Future Business Models and Value Propositions, Products and Services
- Value Chain Evaluation – Vision, Mission and Strategy Theme contribution to Value
- Evaluated Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions
- ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT •
The underlying premise of Enterprise Risk Management is that every enterprise exists to protect value and conserve assets for its stakeholders. All entities face uncertainty and the possibility of chaos and disruption. Risk Management is the evaluation of that uncertainty.
The challenge is to determine how much risk we can accept as we strive to grow stakeholder value. Uncertainty presents both opportunity and risk with the possibility of either erosion or enhancement of value.
Strategic Foresight enables stakeholders to deal effectively with uncertainty and the associated risk and opportunity that uncertainty brings – thus enhancing the capability of the Enterprise to secure long-term stakeholder value through Enterprise Risk Management •
Enterprise Risk Management – Value Chain Management: –
- Enterprise Risk Management
- Risk Research and Identification
- Risk Analysis, Assessment and Prioritisation
- Risk Planning, Mitigation and Management
- Value Chain – Risk Modelling – Cash Flow Protection and Asset Conservation
- Modelled Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions
Systemic Risk (external threats)
- Political Risk – Political Science, Futures Studies and Strategic Foresight
- Economic Risk – Fiscal Policy, Economic Analysis, Modelling and Forecasting
- Wild Card Events – Horizon Scanning, Tracking and Monitoring – Weak Signals
- Black Swan Events – Scenario Planning & Impact Analysis – Future Management
Market Risk (macro-economic threats)
- Currency Risk – FX Curves and Forecasting
- Commodity Risk – Commodity Price Curves and Forecasting
- Interest Rate Risk – Interest Rate Curves and Forecasting
- Equity Risk – Traded Instrument Product Analysis and Contract Management
Trade Risk (micro-economic threats)
- Credit Risk – Debtor Analysis and Management
- Liquidity Risk – Solvency Analysis and Management
- Insurance Risk – Underwriting, Due Diligence and Compliance
- Counter-Party Risk – Counter-Party Analysis and Contract Management
Operational Risk (internal threats)
- Legal Risk – Contractual Due Diligence and Compliance
- Statutory Risk – Legislative Due Diligence and Compliance
- Regulatory Risk – Regulatory Due Diligence and Compliance
- Competitor Risk – Competitor Analysis, Defection Detection / Churn Management
- Reputational Risk – Internet Content Scanning, Intervention / Threat Management
- Corporate Responsibility – Enterprise Governance, Audit, Reporting and Controls
Digital Communications and Technology Risk
- Security Risk – Security Principles and Policies, Security Models and Architecture
- Process Risk – Business Process Management, Process Models and Architecture
- Information Risk – Information Strategy Models, Roadmaps and Architecture
- Technology Risk – Technology Strategy Models, Roadmaps and Architecture
- Stakeholder Risk – Benefits Realisation Strategy and Communications Management
- Vendor / 3rd Party Risk – Strategic Vendor Analysis and Supply Chain Management
- STRATEGY PLANNING •
Strategy Planning is the bridge between the VISION and the ACTION – the “ACTION LINK”
Here, the Strategy team transforms the desired Vision, Missions, Outcomes, Goals and Objectives into the Strategic Master Plan, Enterprise Landscape Models, Strategic Roadmaps and Transition Plans for organisational readiness and mobilisation – maintaining Strategic Foresight mechanisms (Horizon Scanning, Monitoring and Tracking, Scenario Planning and Impact Analysis) to preserve the capability to react quickly to fluctuations and change impacting internal environments along with the capacity to rapidly respond to unexpected disruptive and chaotic events in external environments •
Strategy Planning: –
- Digital Strategy Themes and Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Competitor Positioning and Rival Market Value Propositions (MVPs)
- Value Chain Management – Auditable Cash Flow and Value Chain Models
- Planned Future Business Models and Value Propositions, Products and Services
- Strategic Master Plan, Enterprise Landscape Models, Roadmaps and Transition Plans
- Managed Assumptions, Critical Success Factors, Strategy Themes and Value Propositions
- STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION
This penultimate phase is about communicating results and developing action agendas for mobilising strategy delivery – thus launching Digital Business Transformation Programmes that will drive forwards to the realisation of Strategic Master Plans and Future Business Models through Digital Business Transformation, Enterprise Portfolio Management, Technology Refreshment and Service Management – via Cultural Change, innovative multi-tier and collaborative Business Operating Models, Emerging SMAC Digital Technologies (Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud Services) Business Process Re-engineering and Business Process Outsource (BPO) – Onshore / Offshore.
Strategy Implementation: –
- Digital Market Value Propositions (MVPs) Launched
- Value Chain Management – Cash Flow and Value Chain Management Systems
- Digital Business Models and Value Propositions, Products and Services Introduced
- Programme Master Plan, Enterprise Landscape Models, Roadmaps and Transition Plans
Digital Business Transformation – Implementation, Enablement and Delivery Programmes: –
- Digital Business Transformation – Organisational Re-structuring • Cultural Change • Business Process Management • Operating Models • Programme Planning, Management, Controls
- DCT Models – Demand / Supply Models • Shared Services • Business Process Outsource
- Enterprise Portfolio Management – Technology Refreshment • System Management •
- Launched Future Business Models and Value Propositions, Digital Products and Services
- Emerging Technologies – Social Intelligence • Mobile Computing • Smart Devices • Analytics • Artificial Intelligence • Cloud Services • Telemetry Smart Grid • Geospatial Data Science •
- Digital Service Management – Service Planning • Service Brokering • Service Access • Service Provisioning • Service Delivery • Cash Flow Analysis and Value Chain Management •
- STRATEGY REVIEW •
In this final phase, we focus on Key Lessons Learned and maintaining the flow of useful information from the Strategic Foresight mechanisms and infrastructure – to support an ongoing lean and agile capability to continually and successfully respond to the volatile and dynamic internal and external environment – through Strategic Foresight, Strategy Reviews, Business Planning and Forecasting
Strategy Review: –
- Reviewed Business Models and Value Propositions, Products and Services
- Futures Studies, Strategy Reviews, Business Planning and long-range Forecasting
- Horizon Scanning, Monitoring and Tracking – Cloud Systems, Infrastructure and Data
- Scenario Forecasting and Impact Analysis – Cloud Systems Infrastructure and Data
We can now prepare again for the beginning of the next round of the Strategy Cycle, beginning once more with Phase 1 – Framing and Scoping.
SUMMARY
Creative Destruction through Technology Disruption describes the incessant process of Economic Restructuring through Technology Innovation – the mechanism by which new and more efficient methods of production for novel and attractive products and services in emerging industries attracts investment capital at a greater rate than the outdated and less efficient methods of production for heritage products and services in legacy industries.
This cumulative microeconomic activity exerts a major influence over all aspects of macroeconomic performance – from long-term economic growth to the short-term cyclical business fluctuations and structural adjustments in markets. “Rising
Star” digital industries will yield a better return on investment than older legacy industries – and so will out-perform, overtake and ultimately replace them.
Over the long term, Economic Restructuring – Creative Destruction through Technology Disruption – accounts for over 50 per cent of growth in economic output, the remainder is due to natural organic growth in older “Cash Cow” industries.
CONCLUSION
The paradox of Digital Business Transformation is that Society cannot reap the benefits of Economic Restructuring – the rewards from the incessant process of Creative Destruction through Technology Innovation – without accepting that:
There will be both winners and losers in this process. Those mobile, agile and skilled individuals with enhanced digital competencies and qualities who are more able to exploit the new economic opportunities being created in the Digital Economy – will prosper, in both their careers and personal lives.
Those individuals and their families who are less mobile, agile and skilled may feel worse off as legacy industries decline and traditional jobs disappear – not just in the short term, but perhaps becoming disadvantaged and isolated for the rest of their lives.

Article by channel:
Everything you need to know about Digital Transformation
The best articles, news and events direct to your inbox